Three functional domains of neurons include:
- The Axon -- a cellular extension that projects to, and makes synapses with, the dendrites of other neurons
- Dendrites -- extend from the cell body and receive input from other neurons
- Cell Body -- a globular compartment containing a variety of organelles including the nucleus, and gives rise to the axon and dendrites
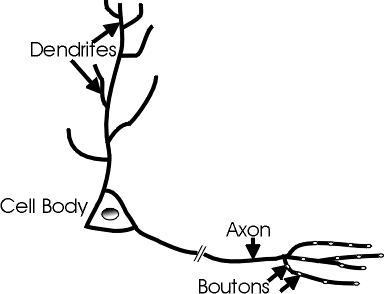
Axons typically project over long distances from their sites of origin to communicate and synapse with their targets. Swellings termed axonal varicosities / boutons are typically the sites where synapses occur. Boutons form as terminal bulbs at the end of an axon, and/or along the length of individual axons as boutons en passant (see diagram left). Axonal bouton, varicosity, en passant terminal or bouton are terms often used interchangeably, although they may exist as slightly different morphological entities.

Axon Coursing Through Apical Dendrites of a CA1 Pyramidal Neuron
An axon can be either myelinated or unmyelinated. Within the central nervous system, glial cells termed oligodendrocytes form the myelin sheath around axons and serve to facilitate synaptic transmission along their length. Oligodendrocytes are non-neuronal cells and their cell bodies can be found within hippocampal area CA1.

Individual axons and their boutons occur in a variety of shapes, sizes and contain a number of functionally important intracellular organelles. For example, the following organelles can be easily identified within axons:
- microtubules
- endoplasmic reticulum
- synaptic vesicles
- dense core vesicles
- coated vesicles
- multivesicular body
- mitochondria
Axonal boutons can be classified relative to their synaptic vesicle characteristics. Here is a summary table of axons found in hippocampal area CA1. These data are likely transferable to a variety of brain regions.
Individual boutons form either single (SSB) or multiple synapses (MSB) with their postsynaptic partners. Such synaptic relations can be easily studied via rendered reconstructions generated from serial electron micrographs.
A highly complex multiple synapse bouton forming many synapses with its postsynaptic partner is typically described as a synaptic glomerulus.